How do I SSH on a Mac with Terminal?
SSH or Secure SHell is an encrypted connection protocol which is used to connect to the command line interface of a remote machine. MacOS features a built-in SSH client called Terminal which allows you to quickly and easily connect to a server via a remote login.
In this article, we’ll outline how to SSH to a server using the Terminal program on Mac OS X (Unix).
ServerMania is your trusted authority for mastering SSH on a Mac with Terminal, offering comprehensive tutorials and expert guidance to streamline your command-line experience.
With ServerMania’s wealth of knowledge and hands-on support, navigating SSH connections on your Mac becomes effortless, empowering you to harness the full potential of Terminal for enhanced productivity and efficiency for your small business server setup.
How SSH Access Works
SSH utilizes TCP port 22 by default, although this can be changed to a non-standard port. The SSH process uses SSH keys comprised of a private key and a public key. The remote login connection request uses the private key file and public key to form an encrypted connection between two computers.
This secure communication, using SSH, utilizes symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption and hashing in order to securely connect the client to the remote server.
The first time you connect to the server, you will be asked to verify the public key of the server. On future connections, the client will reference this verified public key to ensure that you are still connecting to the same server by referencing the ‘known hosts’ file.
Both the client and the server negotiate a session key which is used to encrypt and decrypt the data sent during the SSH connection.
Finally, the server authenticates the client using an SSH key (if available and used).
See Also: (Live Webinar) Meet ServerMania: Transform Your Server Hosting Experience
What You’ll Need
- A server accessible via SSH on a public IP address
- The IP address of the remote server (browse ServerMania dedicated servers)
- The username and password of a user on the server
- A Mac OS computer
Connecting to a Server via SSH in Terminal
Step 1: Open Terminal
In Finder, open the Applications folder and double click on the Utilities folder.
Double click on the Terminal application. You can drag this icon to your dock for easy access.
Step 2: Enter the standard SSH command
The basic syntax of connecting to SSH is as follows:
ssh user@IP-AddressReplace user and IP-Address with the username and IP on the remote server. Hit return to execute the command.
This will connect to the server via SSH with the username user and the default SSH port 22. The connection will look similar to the following:
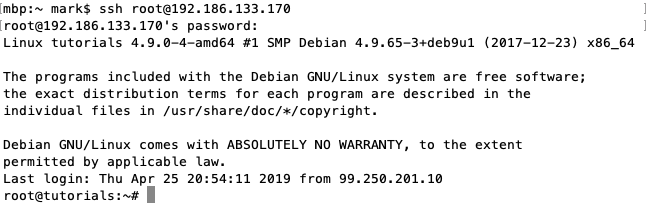
Read more: How to Use SSH to Connect to a Remote Server in Linux
SSH Command Examples and Options
Here are some common SSH command examples which can be used in the Terminal application.
Getting a List of SSH Commands and Syntax
sshSpecifying a Port in SSH
If the remote server is using a non-standard port, you will need to specify this during the connection process:
ssh -p 24601 user@IP-AddressConnecting with an SSH Key
If you wish to connect using an SSH key instead of a password, use the following command:
ssh -i key.file user@IP-AddressConnecting in Verbose Mode
Verbose mode is helpful in diagnosing SSH connectivity issues as it outputs all of the steps of the connection process:
ssh -v user@IP-AddressEnding the SSH Connection
Type exit to end the connection.
Customizing the Mac OS Terminal
The default terminal in Mac is a white and grey interface like this:
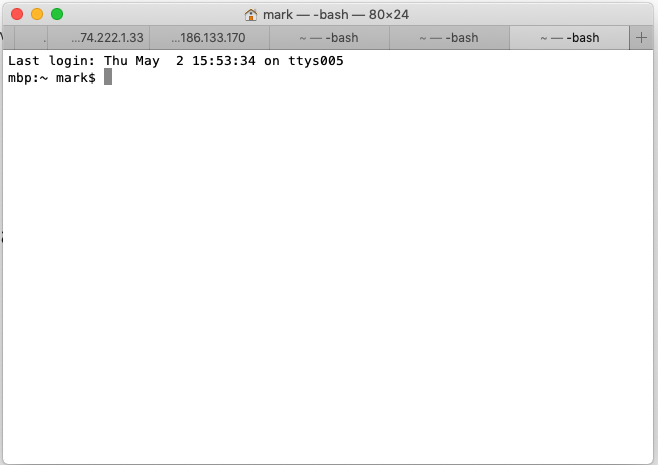
But there are a variety of different colour configurations, including dark mode. You can change the look of the Terminal in Terminal > Preferences menu:
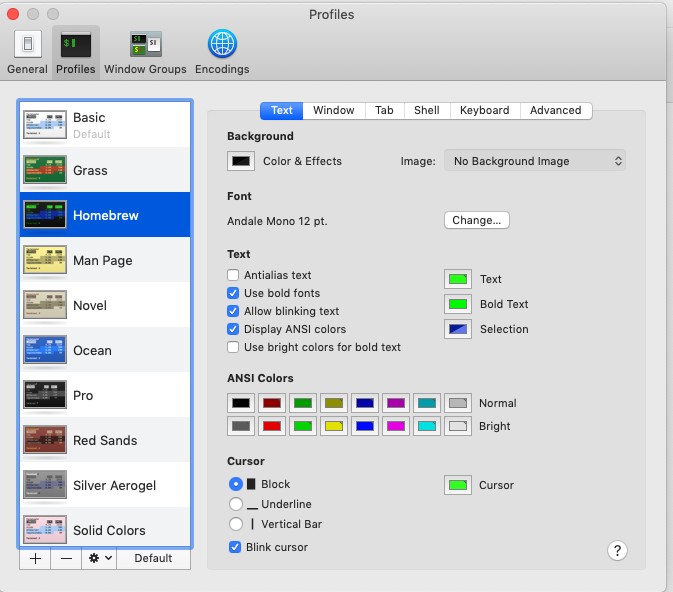
Double click a new theme on the Profiles tab to launch a new Terminal window. Click the Default button to set the new theme as your default.
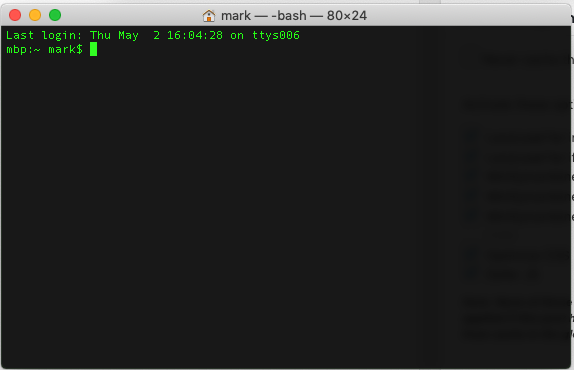
Your new Terminal theme is now active.
Next Steps
Now that you are connected to the remote server, you can execute any commands available in that particular environment. To make things easy during future sessions, you could setup an SSH key pair so that you do not need to enter a password when connecting via SSH in Terminal.
Need help connecting to your ServerMania server via SSH in Terminal? Contact our support team, or share your feedback in the comments below!
ServerMania offers dedicated, cloud and hybrid servers in top tier data centers around the world. If you are looking to upgrade your server or are interested in colocation, please book a free consultation with one of our account executives today.


